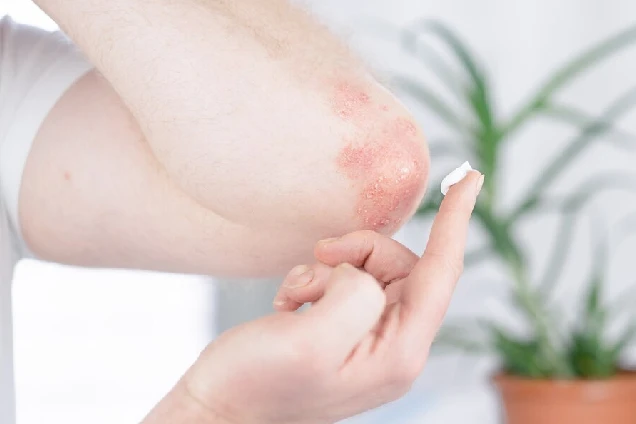
Skin allergies occur when the immune system reacts abnormally to a substance that is typically considered harmless, leading to symptoms like redness, itching, swelling, and rash. These allergic reactions can be triggered by various allergens, such as certain foods, chemicals,sunlight, medications, or environmental factors like dust and pollens.
It's essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and tailored treatment, especially if the allergy is severe or persistent. We at Subodha Skin and Cosmetic clinic, the best dermatology clinic in Bangalore, try to find out the underlying cause of skin allergy and customize the treatment accordingly. Each patient with allergy has different triggers and our expert dermatologists take a detailed history before arriving at a management plan. some blood tests and skin allergy tests may be advised depending on the need to arrive at a proper diagnosis.